lv false tendon | false chord echo lv false tendon Left ventricular (LV) false tendons have been a bit of an enigma since they were first described by Turner in 1896.1 They are bands traversing the LV cavity and arise embryologically from the same layer as trabeculations but are distinguished by being free in the LV cavity rather than being adherent to the wall.
$45K+
0 · left ventricular false tendon
1 · false ventricular tendons
2 · false tendons in left ventricle
3 · false tendon lv apex
4 · false chordae tendineae
5 · false chordae left ventricle
6 · false chord echo
7 · calcified false tendon
$10K+
Left ventricular false tendons (LVFTs) are echogenic fibromuscular structures, connecting the left ventricular free wall or papillary muscle and the ventricular septum. As they are not related to the mitral valve apparatus, the term “false” tendon is in use. Left ventricular (LV) false tendons are chordlike structures that traverse the LV cavity. They attach to the septum, to the papillary muscles, or .
Left ventricular (LV) false tendons have been a bit of an enigma since they .Left ventricular false tendons (LVFTs) are echogenic fibromuscular structures, connecting the left ventricular free wall or papillary muscle and the ventricular septum. As they are not related to the mitral valve apparatus, the term “false” tendon is in use.
Left ventricular (LV) false tendons are chordlike structures that traverse the LV cavity. They attach to the septum, to the papillary muscles, or to the free wall of the ventricle but not to the mitral valve. They are found in approximately half . Left ventricular (LV) false tendons have been a bit of an enigma since they were first described by Turner in 1896.1 They are bands traversing the LV cavity and arise embryologically from the same layer as trabeculations but are distinguished by being free in the LV cavity rather than being adherent to the wall.
Left ventricular false tendons (LVFTs) are chord-like structures that traverse the LV cavity and are generally considered to be benign. However, they have been associated with arrhythmias, LV hypertrophy and LV dilation in some small studies.False tendons play an important role in the genesis of LPF-VT. Guided by ICE imaging, a “culprit FT” can be identified when a P1 or earliest P2 is recorded using a MEC adjacent to the FT during tachycardia.
Left ventricular false tendons (LVFT) are common structures visualized on transthoracic echocardiography (TTE). The present study tested the hypothesis that LVFT, via a possible ‘constraint’ mechanism, attenuate left ventricular (LV) remodeling and secondary mitral regurgitation after acute myocardial infarction.
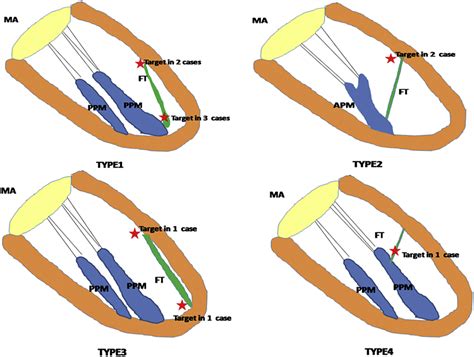
Left ventricular false tendons (LVFTs) are fibrous or fibromuscular bands stretching across the left ventricle (LV) from the ventricular septum to the papillary muscle or LV free wall but not connecting, like the chordae tendinae, to the mitral leaflet.LVFTs is a useful anatomical landmark of LV for the differentiation of morphological LV and right ventricle in segmental analysis of congenital heart disease. LVFTs are a cause of functional murmur. No pressure gradient was noted in the mid-LV or outflow tract. Left ventricular (LV) false tendons (FTs) traverse the ventricular cavity and are found in 25% of patients echocardiographically 1 and in 35% at autopsy. 2 These structures interconnect ventricular walls or papillary muscles or course from 1 to the other. 3 LVFTs vary from thin fibrous strings to thick muscular bands (Figure 1), which harbor myo. Left ventricular false tendons are frequently localized between the middle segments of the inferior septum and the lateral wall and are statistically associated with ventricular repolarization abnormalities. Keywords: Repolarization anomalies, T wave inversion, Young athletes, False chordae tendineae, Echocardiography.
Left ventricular false tendons (LVFTs) are echogenic fibromuscular structures, connecting the left ventricular free wall or papillary muscle and the ventricular septum. As they are not related to the mitral valve apparatus, the term “false” tendon is in use.

the bay michael kors suits
left ventricular false tendon
Left ventricular (LV) false tendons are chordlike structures that traverse the LV cavity. They attach to the septum, to the papillary muscles, or to the free wall of the ventricle but not to the mitral valve. They are found in approximately half . Left ventricular (LV) false tendons have been a bit of an enigma since they were first described by Turner in 1896.1 They are bands traversing the LV cavity and arise embryologically from the same layer as trabeculations but are distinguished by being free in the LV cavity rather than being adherent to the wall.
Left ventricular false tendons (LVFTs) are chord-like structures that traverse the LV cavity and are generally considered to be benign. However, they have been associated with arrhythmias, LV hypertrophy and LV dilation in some small studies.False tendons play an important role in the genesis of LPF-VT. Guided by ICE imaging, a “culprit FT” can be identified when a P1 or earliest P2 is recorded using a MEC adjacent to the FT during tachycardia.Left ventricular false tendons (LVFT) are common structures visualized on transthoracic echocardiography (TTE). The present study tested the hypothesis that LVFT, via a possible ‘constraint’ mechanism, attenuate left ventricular (LV) remodeling and secondary mitral regurgitation after acute myocardial infarction.
Left ventricular false tendons (LVFTs) are fibrous or fibromuscular bands stretching across the left ventricle (LV) from the ventricular septum to the papillary muscle or LV free wall but not connecting, like the chordae tendinae, to the mitral leaflet.
LVFTs is a useful anatomical landmark of LV for the differentiation of morphological LV and right ventricle in segmental analysis of congenital heart disease. LVFTs are a cause of functional murmur. No pressure gradient was noted in the mid-LV or outflow tract. Left ventricular (LV) false tendons (FTs) traverse the ventricular cavity and are found in 25% of patients echocardiographically 1 and in 35% at autopsy. 2 These structures interconnect ventricular walls or papillary muscles or course from 1 to the other. 3 LVFTs vary from thin fibrous strings to thick muscular bands (Figure 1), which harbor myo.
false ventricular tendons
alek wek wearing michael kors collection

Rolex Submariner Yellow gold. Rolex Submariner Date. from $7,509. Rolex Submariner (No Date) from $7,944. Rolex Submariner (1990-2010) from $39. Rolex Submariner .
lv false tendon|false chord echo