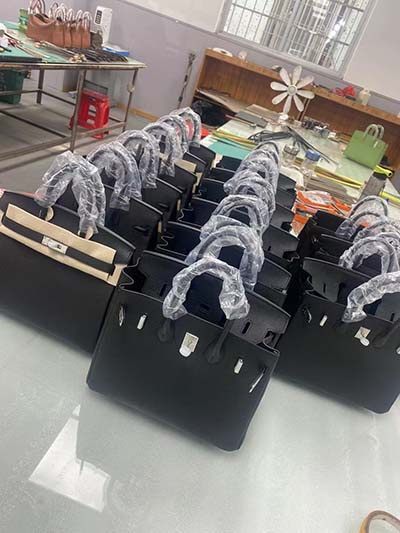
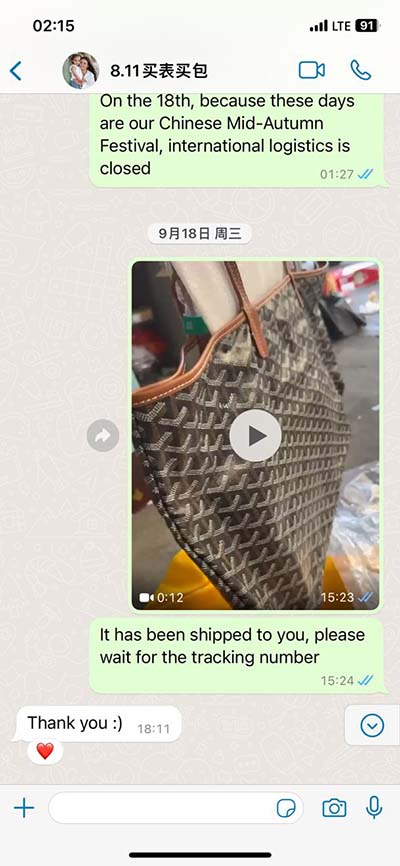
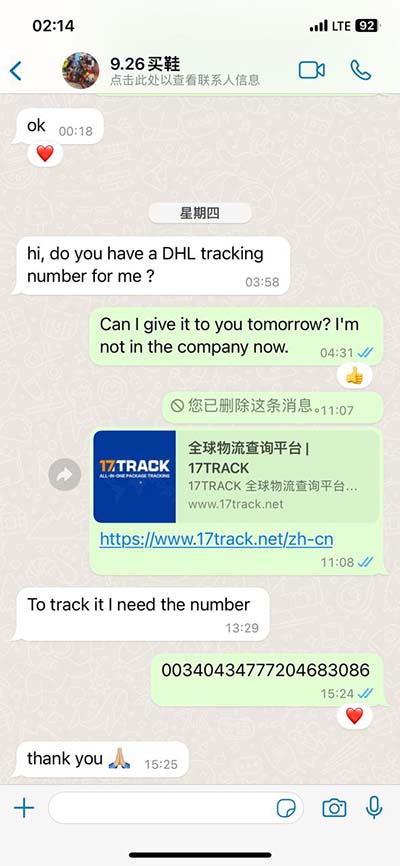
hermes healing | mythology of hermes hermes healing For Carl Jung, Hermes's role as messenger between realms and as guide to the underworld made him the god of the unconscious, . See more THE TOP WATCH REVIEWS OF 2021 – The Cartier Tank Must Collection (#11) Editor’s note: The Time+Tide team reviewed hundreds of watches in 2021. Here we count down the Top 30 reviews of the year that you liked best judging by the online traffic. At number 11, it’s the Cartier Tank Must Collection.
0 · mythology of hermes
1 · how did hermes protect himself
2 · how did hermes kill hades
3 · how did hermes get angry
4 · how did hermes fall in love
5 · hermes in the 6th century
6 · hermes in ancient greece
7 · hermes characteristics wikipedia
$8.99
mythology of hermes
Hermes is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology considered the herald of the gods. He is also widely considered the protector of human heralds, travelers, thieves, merchants, and orators. He is able to move quickly and freely between the worlds of the mortal and the divine aided by his . See more
The earliest form of the name Hermes is the Mycenaean Greek *hermāhās, written 𐀁𐀔𐁀 e-ma-a2 (e-ma-ha) in the Linear B syllabic script. Most . See moreHermes began as a god with strong chthonic, or underworld, associations. He was a psychopomp, leader of souls along the road between . See moreAtlantiadesHermes was also called Atlantiades (Greek: Ατλαντιάδης), because his mother, Maia was the daughter of Atlas.ArgeïphontesHermes's epithet Argeïphontes (Ancient Greek See more
goyard long wallet green
how did hermes protect himself
For Carl Jung, Hermes's role as messenger between realms and as guide to the underworld made him the god of the unconscious, . See more
The image of Hermes evolved and varied along with Greek art and culture. In Archaic Greece he was usually depicted as a mature man, bearded, and dressed as a traveler, herald, or shepherd. This image remained common on the Hermai, which served as . See moreIn the Mycenaean periodThe earliest written record of Hermes comes from Linear B inscriptions from Pylos, Thebes, and Knossos dating to the Bronze Age See moreEarly Greek sourcesHomer and HesiodHomer and Hesiod portrayed Hermes as the author of skilled . See more This article aims to explore the myths associated with Hermes and their significant impact on ancient medicine, shedding light on how these narratives shaped healing practices .
Hermes (/ ˈ h ɜːr m iː z /; ‹See Tfd› Greek: Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology considered the herald of the gods. He is also widely considered the protector of human heralds, travelers, thieves, [2] merchants, and orators.
This article aims to explore the myths associated with Hermes and their significant impact on ancient medicine, shedding light on how these narratives shaped healing practices and medical thought in ancient Greece.The snake, which periodically molts, or sheds its skin, is a symbol of healing, regeneration and renewal. In ancient Greece snakes, which move about without any visible means of support or locomotion, were considered to be the wisest and cleverest of all animals. Hermes is renowned for various roles and attributes, including: Messenger of the Gods : He delivered messages between the divine and mortal realms. Trickster : His cleverness and cunning nature often led him to outsmart other gods and mortals.
The caduceus (☤; / k ə ˈ dj uː ʃ ə s,-s i ə s /; Latin: cādūceus, from ‹See Tfd› Greek: κηρύκειον kērū́keion "herald's wand, or staff") [b] is the staff carried by Hermes in Greek mythology and consequently by Hermes Trismegistus in Greco-Egyptian mythology.The caduceus is the traditional symbol of Hermes and features two snakes winding around an often winged staff. It is often used as a symbol of medicine, especially in the United States. Ancient sources associate Hermes with a variety of attributes, including wisdom, trade, deception, thievery, eloquence, negotiation, and alchemy. [1] [2] In Greek mythology, Hermes' staff is an interesting serpent-bearing staff carried by Hermes, the ambassador of the Olympian Gods. The staff is called a caduceus. Sometimes known as the wand of Hermes’, the staff was a powerful weapon symbolizing peace and rebirth.
goyard mini alpine
Originally associated with Hermes, the Greek messenger god, the Caduceus features two serpents entwined around a winged staff. This symbol is frequently confused with the Rod of Asclepius, a symbol traditionally linked to healing and medicine.
The hermes symbol, the caduceus wand, has been heavily incorporated into medical symbols, associated with the messenger of the gods, conveying its importance as a symbol of healing. The modern meaning of the caduceus is associated with health promotion, showing a connection between the healthcare and the divine.
Hermes is the Greek God of healing. Known to the Romans as Mercury. Also the God of comunication, boundries, merchants, commerce, theives, athletes and travel. He was known as the patron of travellers, as doctors had to travel great distances to treat patients.
Hermes (/ ˈ h ɜːr m iː z /; ‹See Tfd› Greek: Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology considered the herald of the gods. He is also widely considered the protector of human heralds, travelers, thieves, [2] merchants, and orators. This article aims to explore the myths associated with Hermes and their significant impact on ancient medicine, shedding light on how these narratives shaped healing practices and medical thought in ancient Greece.The snake, which periodically molts, or sheds its skin, is a symbol of healing, regeneration and renewal. In ancient Greece snakes, which move about without any visible means of support or locomotion, were considered to be the wisest and cleverest of all animals. Hermes is renowned for various roles and attributes, including: Messenger of the Gods : He delivered messages between the divine and mortal realms. Trickster : His cleverness and cunning nature often led him to outsmart other gods and mortals.
The caduceus (☤; / k ə ˈ dj uː ʃ ə s,-s i ə s /; Latin: cādūceus, from ‹See Tfd› Greek: κηρύκειον kērū́keion "herald's wand, or staff") [b] is the staff carried by Hermes in Greek mythology and consequently by Hermes Trismegistus in Greco-Egyptian mythology.The caduceus is the traditional symbol of Hermes and features two snakes winding around an often winged staff. It is often used as a symbol of medicine, especially in the United States. Ancient sources associate Hermes with a variety of attributes, including wisdom, trade, deception, thievery, eloquence, negotiation, and alchemy. [1] [2]
In Greek mythology, Hermes' staff is an interesting serpent-bearing staff carried by Hermes, the ambassador of the Olympian Gods. The staff is called a caduceus. Sometimes known as the wand of Hermes’, the staff was a powerful weapon symbolizing peace and rebirth. Originally associated with Hermes, the Greek messenger god, the Caduceus features two serpents entwined around a winged staff. This symbol is frequently confused with the Rod of Asclepius, a symbol traditionally linked to healing and medicine. The hermes symbol, the caduceus wand, has been heavily incorporated into medical symbols, associated with the messenger of the gods, conveying its importance as a symbol of healing. The modern meaning of the caduceus is associated with health promotion, showing a connection between the healthcare and the divine.

how did hermes kill hades

$6,350.00
hermes healing|mythology of hermes